Agriculture production is heavily reliant on water and is becoming increasingly vulnerable to water scarcity. It is also the leading consumer of energy and a significant polluter of water.
Water management in agriculture must therefore be improved in order for the agro-food sector to be sustainable and productive.
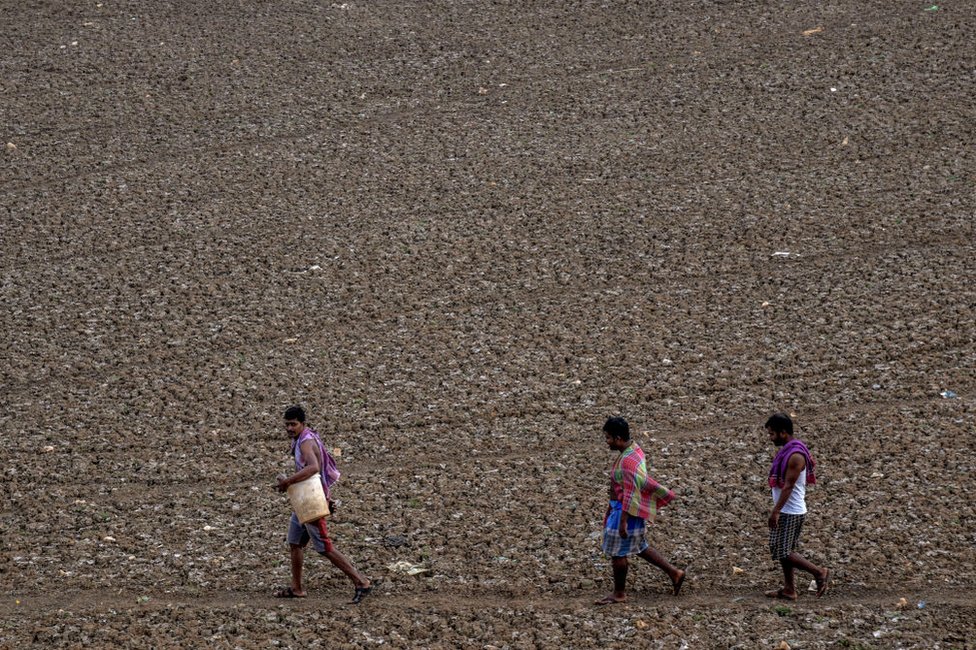

Water scarcity has become increasingly severe in agricultural regions around the world in recent years. Droughts in Chile and the United States have harmed agricultural output and depleted surface and groundwater supplies.
These, as well as other extreme weather events such as floods and tropical storms, are anticipated to become more common.
Climate change is expected to increase variability in precipitation and surface water supplies, diminishing snowpack and glaciers and influencing crop water needs.
Basically, Water scarcity is defined as an imbalance between freshwater availability and demand, in which demand surpasses supply.
The Crisis
According to the report, which was produced by the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the International Water Management Institute’s Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE) program, exploding demand for food with high environmental footprints, such as meat from industrial farms, is contributing to unsustainable agricultural intensification and water-quality degradation.
Agricultural pollution has replaced contamination from cities and industry as the dominant driver in the degradation of inland and coastal waters in most high-income nations and many emerging economies, according to Eduardo Mansur, Director of FAO’s Land and Water Division.
“The first step in finding solutions is admitting we have a problem.” Aquaculture has also increased by more than 20 times since the 1980s, mainly in Asia. In 2014, total global aquatic animal production was 167 million tonnes.
Water quality is harmed by fish excrement and uneaten feeds from fed aquaculture. Increased production has coincided with increased usage of antibiotics, fungicides, and anti-fouling chemicals, all of which could pollute downstream ecologies.

BWS And GWS
Because it underpins the rising rivalry between water uses for societal and environmental purposes, blue water has been at the center of the water scarcity discussion.
Also, the Green water scarcity (GWS) in crop production refers to a situation in which the rainfall regime is unable to supply the crop water requirements.
That is, irrigation is required for at least part of the year to prevent water-limited crop growth. BWS is becoming more widely recognized as a global socio-environmental issue linked to concerns about food and energy security.
Green water, on the other hand, has received far less attention, despite the fact that it contributes 65 percent of global crop production.
The Sustainable Development Goals agenda still lacks a green water management plan. Economic water scarcity has received even less attention (EWS).

Incentivization
The correct policies and incentives can support more sustainable and healthful diets, hence reducing food demand growth.
For example, monetary incentives such as food taxes and subsidies, as well as consumer discounts, have a favorable impact on dietary behavior.
To reduce resource waste and associated environmental implications, food losses and waste should be reduced. In addition, a broader spectrum of policy solutions addressing other issues has emerged.
A combination of techniques (regulations, economic incentives, and knowledge) is more effective than a single approach, As Per the recent studies
Also Read: Crop Diversification Is A Sure Requirement In India











